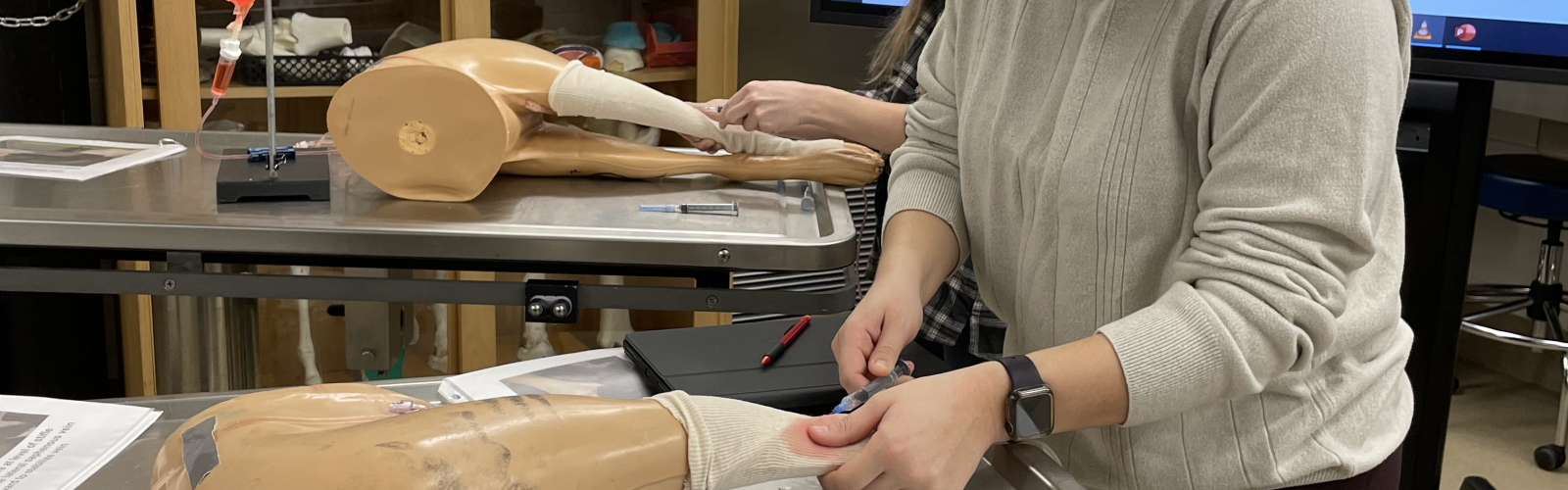
Instructional Models
Equine Distal Limb and Foot Models
High-fidelity equine models created to reinforce the complex anatomy of the distal limb, including tendons, pulse points and nerve blocks. Related supportive content was created for use during active learning labs.
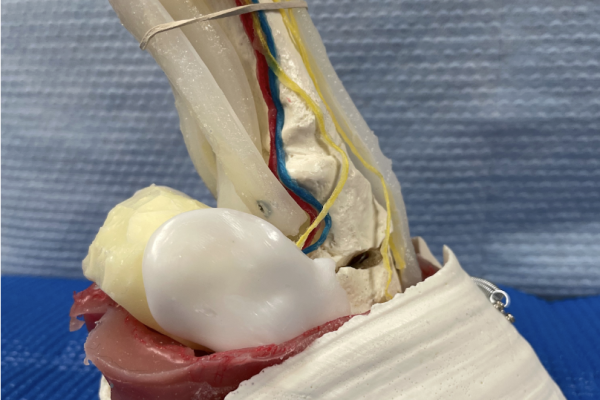
Descent of Feline Testicles Model
Feline model demonstrating the topography and structures related to the testicles when they are intra-abdominal and as they descend into the scrotum. This model facilitates discussion about cryptorchidism, the peritoneal cavity and related tunics.
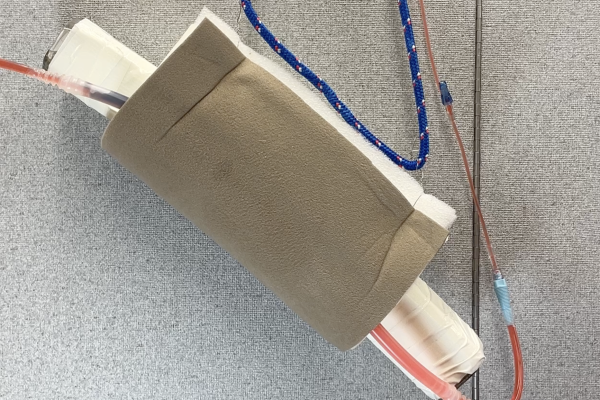
Large Animal Jugular Vein Model
Low-fidelity jugular model designed specifically to teach the hand mechanics of jugular vein access (blood withdrawal, medication administration as well as placing and securing an IV catheter) in a large animal patient.
Extrinsic muscles of the forelimb model
Low-fidelity model demonstrating the attachments, topography and functions of the extrinsic muscles of the canine forelimb. Model used in anatomy to include discussion of the transection of these muscles during forelimb amputation (clinical context).
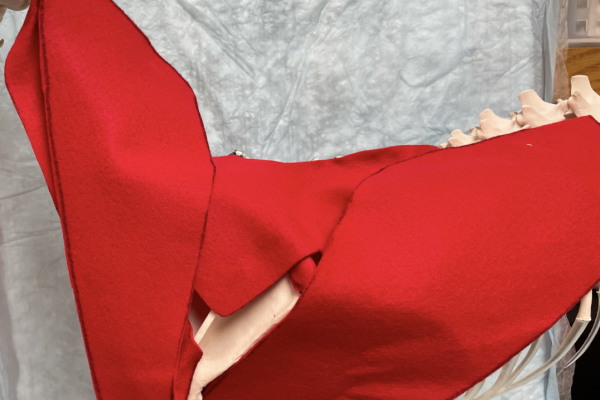

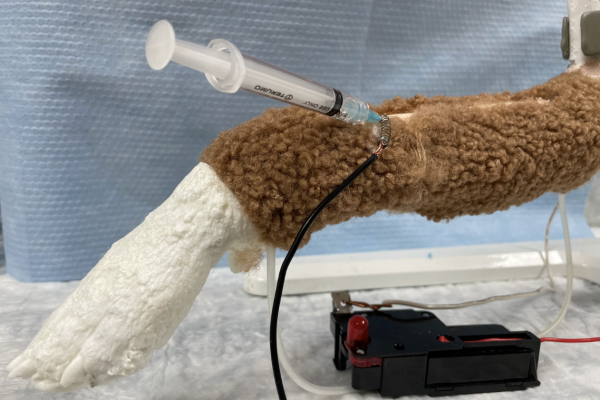
Intravenous access model (Operation® game circuit)
Clinical skill building dog/cat limb intravenous model incorporating an Operation® board game circuit to provide negative feedback (buzzer) when IV access is unsuccessful while red fluid provides positive feedback when the vein is properly accessed.

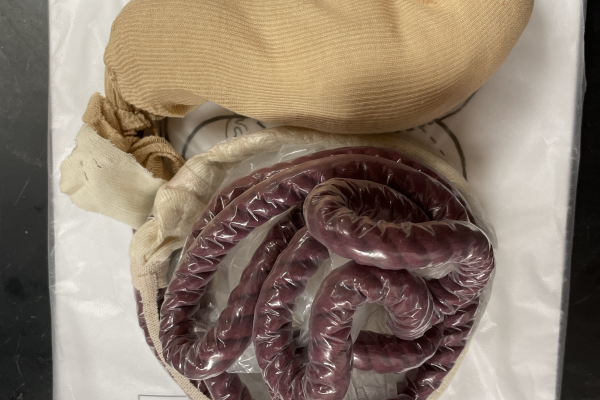
Gastrointestinal (GI) Topographic Model
Low-fidelity GI model that students assemble in order to highlight topographic interrelationships between abdominal structures.

Canine Intestinal Model
This is a silicone based model that is meant to mimic the small intestine of a medium to large breed canine. It is designed to teach clinical and surgical skills related to an enterotomy and intestinal resection and anastomosis.
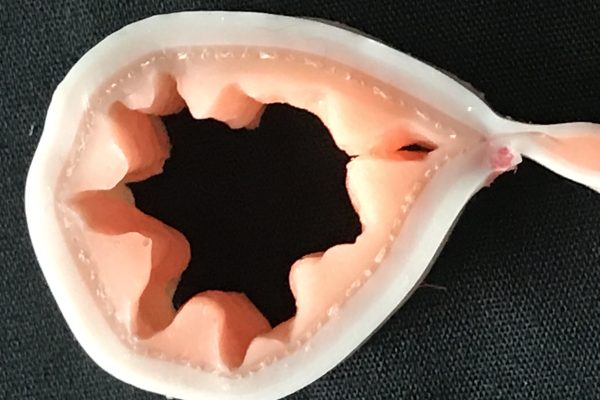
Bovine Foot Models
Plastic models used in the large animal anatomy course as part of an active learning exercise.
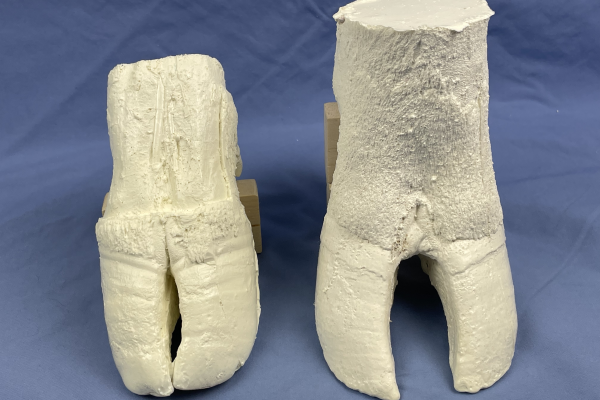
Feline Castration Models
First and second generation feline castration models are demonstrated. First generation models used in clinical skill development. Second generation is in prototype form at the moment, but being actively developed now.
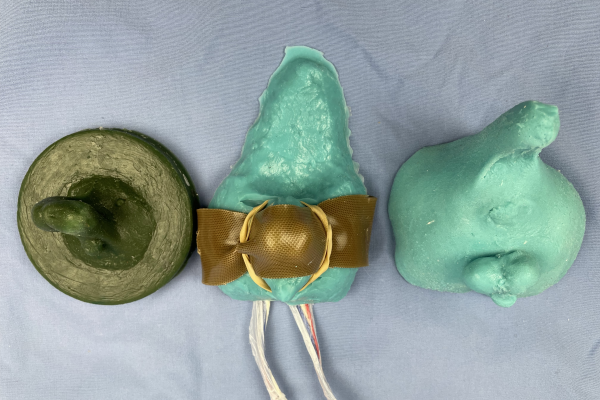
Canine Neuter Model
Canine neuter model with reusable resin base, replaceable silicone skin and foam testicles, as well as a reusable silicone anesthetic block model. Allows for practice of all related clinical skills.
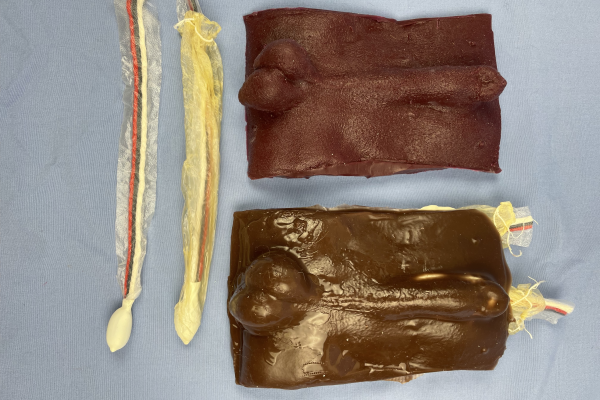
Blood Flow Through the Uterus Model
This model is used in an active learning activity for small animal anatomy. It is used to reinforce the anatomy and topography of the female reproductive tract in a clinically relevant context- an ovariohysterectomy (OHE)/spay surgical procedure.
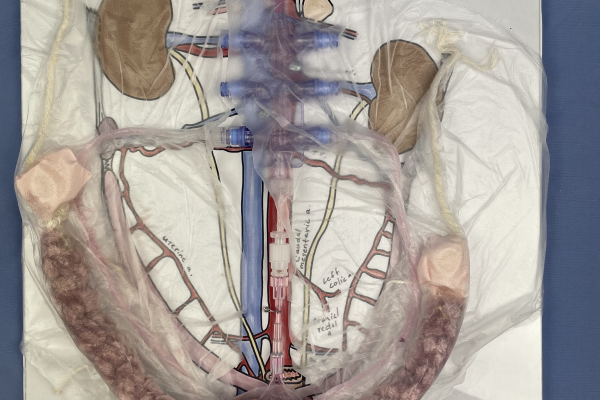
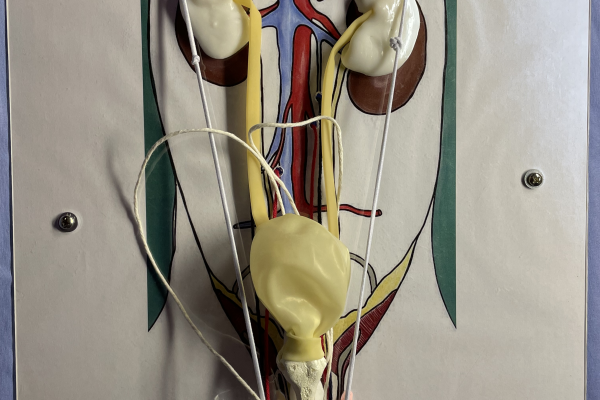
Building the Female Urogenital Tract Model
This model is completed in our small animal anatomy course as an active learning exercise (ALE). It is one of many active learning exercises that stress the topographic relationships and vasculature of the pelvic and abdominal cavities.
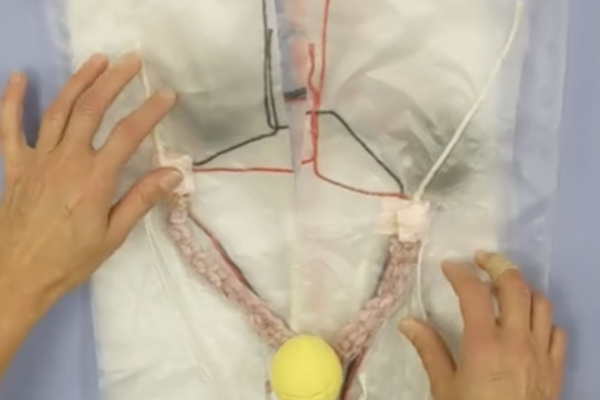
Epaxial Intramuscular Injection Model
Small animal epaxial injection model that can stand alone or be applied to stuffed animals to teach the clinical skill and allow deliberate practice.
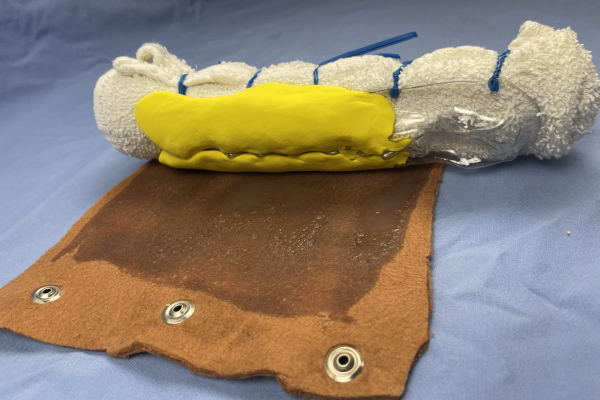
Feline Cystocentesis Models
Low and medium fidelity feline cystocentesis model used in anatomic and clinical skill building courses.

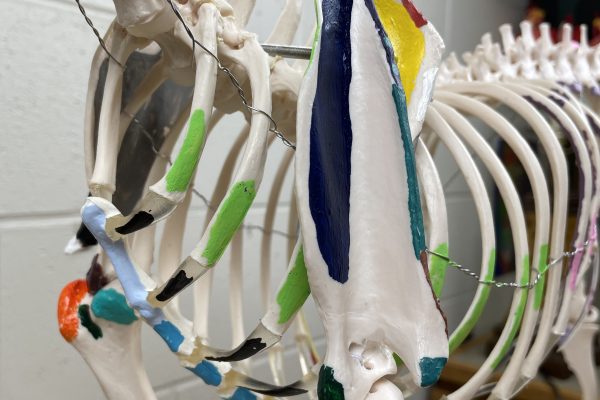
Painted Skeleton Models
Store bought plastic canine skeletons featuring painted color coordinated bony prominences and palpable landmarks on the right side and color coordinated muscular attachments on the right side.

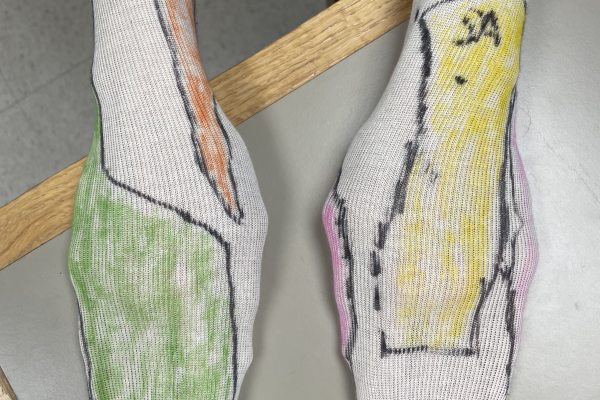
Canine Autonomous Zones & Reflexes
Students create autonomous zone socks for the fore and hind limbs (model creation), watch instructional videos on reflex testing and discuss innervation to the distal limbs in a clinical context in this active learning exercise.

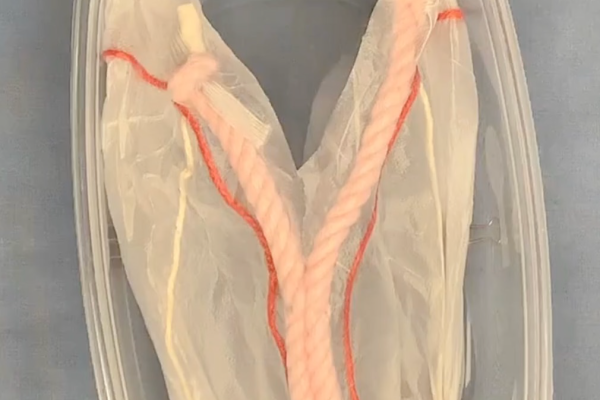
Badger Spay Model
OHE model designed for repeated practice of surgical skills related to an ovariohysterectomy procedure in order to build skill, confidence and muscle memory. Developed from inexpensive materials and is easy to reproduce.

During our active learning exercises, we focus on fully engaging students, so they can immerse themselves in the language, skills, and concepts of the materials they study and become members of the teaching and learning community. Diversity of experiences and perspectives is vital to the success of this community. Designing activities that provide adequate time, space and opportunity for inclusion and dissemination of this diversity and knowledge is paramount to the process.
The document below outlines the expectations for the learning community during participation of our active learning exercises (ALEs).
"I think the best way to learn about anything is to try it."
Mae Jemison (doctor, engineer, astronaut)